
One of the most rapidly developing technologies in the textile field today is geotextile. This innovation refers to a permeable geosynthetic material that, when used in contact with soil, can perform several critical functions — including separation, filtration, reinforcement, protection, and drainage.
Geotextiles are made from polypropylene (PP) or polyester (PET) and have a planar structure formed by the interlocking of two or more sets of elements such as yarns, fibers, rovings, or filaments.
A Brief History of Geotextile Development
The first use of geotextiles was recorded in 1950, in the form of woven fabric. A notable early application occurred in 1958, when geotextiles were used in irrigation structures in Florida, USA.
A decade later, non-woven geotextiles made of polyester were developed by Rhone Poulenc Company in France. These materials had a relatively consistent thickness and were applied in dam construction projects across France during the 1970s.
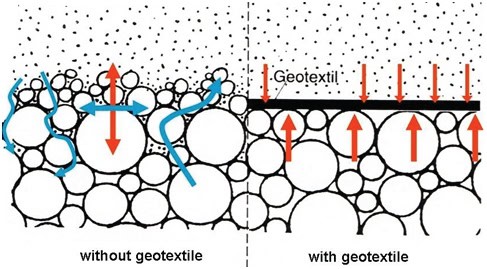
Types of Geotextiles and Their Applications
Woven Geotextile
Woven geotextiles are used for soil separation, load distribution, and ground reinforcement. This material offers high tensile strength, low elongation, and limited deformation under load (up to 15%). It is ideal for applications requiring durability and structural stability.
Non-Woven Geotextile
Non-woven geotextiles are made from randomly arranged fibers bonded together mechanically or chemically. They are widely used for soil separation, ground stabilization, and load distribution, but are less commonly used for retaining wall reinforcement due to their lower tensile strength compared to woven types.
Knitted Geotextile
Knitted geotextiles possess very high tear and tensile strength and can be engineered into customized shapes. This type often incorporates additional fabric layers to form composite geotextiles with enhanced performance characteristics.
Composite Geotextile
Composite geotextiles combine two or more geotextile types (woven, non-woven, or knitted) to achieve specific performance goals, such as improving drainage capacity, reinforcement, or protection functions in specialized construction applications.
Geotextiles represent a synergy between textile engineering and civil construction, providing efficient, sustainable, and long-lasting solutions for soil management and structural reinforcement. As innovation continues, geotextile technology is expected to play an even more vital role in infrastructure development and environmental protection worldwide.